Describe How Carbon Dioxide Emissions Impact Organisms in Aquatic Environments.
Carbon emissions measured in CO2e is a unit that measures the carbon dioxide equivalent that may be released from the chosen human activity. Direct consequences of cumulative post-industrial emissions include increasing global temperature perturbed regional weather patterns rising sea levels acidifying oceans changed nutrient loads and altered ocean circulation.

7 Cartoon Of The Biological Pump Modified From Falkowski And Oliver Download Scientific Diagram
Biomass and biofuels made from biomass are alternative energy sources to fossil fuelscoal petroleum and natural gas.
. Primary energy consumption 94 of total US. The report later states It is extremely likely that more than half of the observed increase in global average surface temperature from. Gaseous exchange - Plants and humans.
To put this into context estimates of life-cycle global warming emissions for natural gas generated electricity are between 06 and 2 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour and estimates for coal-generated electricity are 14 and 36 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour. Vertical section of zonally averaged oxygen changes in the simulation with historical CO 2 emissions and zero emissions from 1 January 2021. It can reduce upper ocean acidification that occurs when carbon dioxide dissolves in seawater making it more difficult for coral and other marine organisms to.
This causes less water to be released diminishing the trees cooling power. Greenhouse gas emissions resulting from human activity. However recent studies underline a second major impact of carbon emissions.
Habitat fragmentation and destruction extinctions biotic homogenization emerging and reemerging pests and pathogens loss of landscape mosaics and connectivity 3. When CO 2 dissolves in sea water it causes the formation of carbonic acid which leads to a fall in pH the pH scale is used to measure acidity 2. The ocean and climate change.
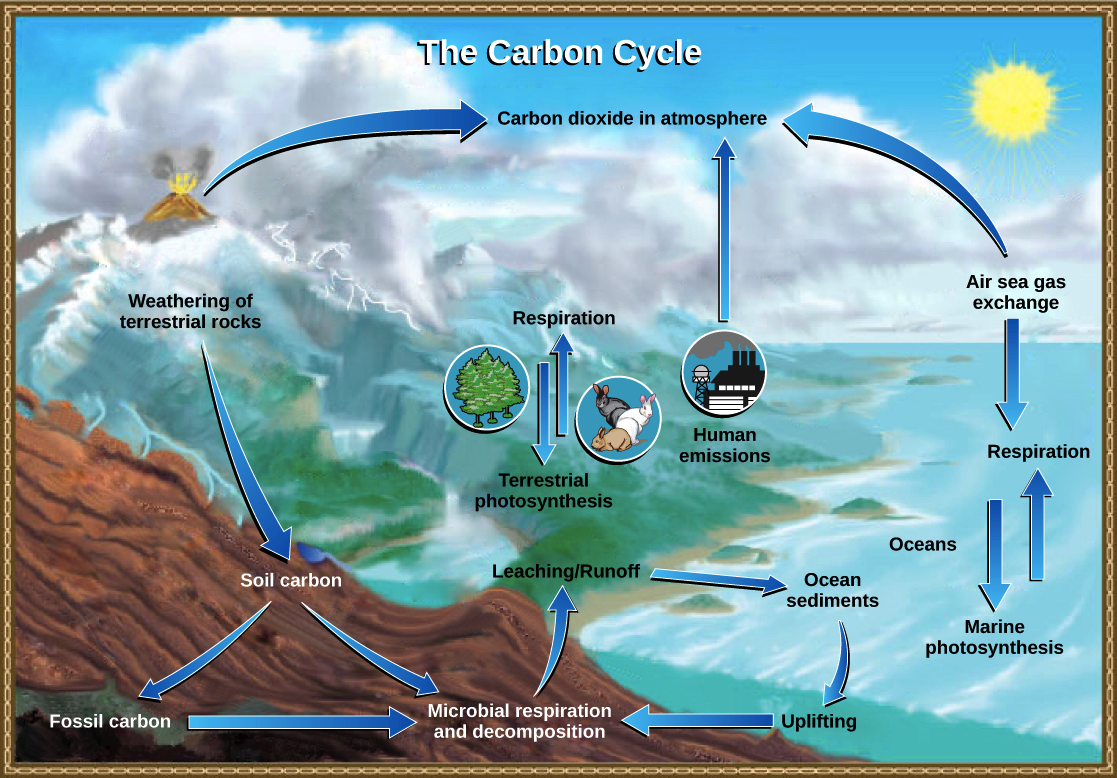
Carbon dioxide occurs naturally as part of the global carbon cycle but human activities have increased atmospheric loadings through combustion of fossil fuels and other emissions sources. Carbon dioxide emissions and 80 of total US. This uptake slows the rise in atmospheric CO 2 considerably thus alleviating climate change caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions.
Water and carbon dioxide combine to form carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 a weak acid that breaks or dissociates into hydrogen ions H and bicarbonate ions HCO 3-. Describe how deforestation leads to an increase in the CO 2 concentration. Aquatic and wetland ecosystems are very vulnerable to climate change.
Regulation of heart rate. The more your carbon footprint goes up the more effect it has on the environment. The effect everyones carbon footprint is having on the environment Carbon footprint is the measure of the amount of plant resources you use.
Using biomass for energy has positive and negative effects. The warming effects of carbon dioxide as a greenhouse gas have been known for a long time says Caldeira. Clams mussels crabs corals and other sea life rely.
Photosynthesis - Calvin Cycle. Transporting food by air emits around 50 times as much greenhouse gases as transporting the same amount by sea. More specifically 0023 kilograms of carbon dioxide-equivalents CO 2 eq per tonne-kilometer by sea versus 113 kilograms CO 2 eq by air.
In 2019 fossil fuels were the source of about 80 of US. The plants absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis through the same pores called stomata. When CO 2 is absorbed by.
The increase in ph levels due to the solubility of carbon dioxide can result in huge long-term effects on carbon based organisms and other marine life higher up in the food chain. Carbon dioxide may affect organisms directly or indirectly. Long-term consequences of carbon dioxide emissions.
Burning either fossil fuels or biomass releases carbon dioxide CO 2 a greenhouse gasHowever the plants that are the source of biomass for energy capture almost the same. If one sees their greenhouse gas emission. The metabolic rates of organisms and the overall productivity of ecosystems are directly regulated by temperature.
The increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide has huge impacts on the solubility of carbon dioxide into earths oceans and as a result alters the ph levels of the seawater. Natural sinks that remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere eg oceans plants help regulate carbon dioxide concentrations but human activities can disturb these. Projected increases in temperature are expected to disrupt present patterns of plant and animal distribution in aquatic ecosystems.
If something harms one part of an ecosystem one species of plant or animal the soil or the water it can have an impact on everything else. The ocean is being disproportionately impacted by increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 and other greenhouse gas emissions GHG from human activities. Photosynthesis - limiting factors.
Describe or explain these effects. This causes changes in water temperature ocean acidification and deoxygenation leading to changes in oceanic circulation and chemistry rising sea levels increased storm intensity as well as. Whether food travels by sea or air makes all the difference.
Haemoglobin and the Bohr shift. An ecosystem is a community of plants animals and other organisms along with their environment including the air water and soil. Then this carbonic acid breaks apart or dissociates producing bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions.
State when the greenhouse effect becomes known as. Over the past 200 years the oceans have taken up 40 of the anthropogenic CO 2 emissions. The ocean absorbs about 30 percent of the CO 2 that is released in the atmosphere and as levels of atmospheric CO 2 increase so do the levels in the ocean.
For example sending a text message emits 001g of CO2e whereas a return plane journey from London to Hong Kong generates 3. Everyday people are doing actives that are producing greenhouse gas emissions. First it forms carbonic acid.
But when carbon dioxide levels are high the leaf pores shrink. Ocean acidification results from an increased concentration of hydrogen ions and a reduction in carbonate ions due to the absorption of increased amounts of CO 2. Carbon dioxide which is naturally in the atmosphere dissolves into seawater.
For more than 200 years or since the industrial revolution the concentration of carbon dioxide CO 2 in the atmosphere has increased due to the burning of fossil fuels and land use change. Overharvest of renewable resources such as fish and timber depleted populations extinctions altered food webs 2. The lower the CO2e the lower the impact the activity has on the environment.
Carbon dioxide and seawater. These and other physical consequences are affecting marine biological processes from genes to ecosystems over scales from rock pools. Because of human-driven increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere there is more.
Everything in an ecosystem is connected. Describe the sources of carbon dioxide emissions and methane emissions greenhouse gases which lead to the greenhouse effect.

Summary Of The Reactions Between Carbon Dioxide Co2 With Water H2o Download Scientific Diagram
Fish Carbon Blue Climate Solutions

Comments
Post a Comment